ESD (ElectroStatic Dissipative) COATINGS REDUCE RISK OF SUDDEN ELECTRIC DISCHARGE
Want to learn more about ESD coatings after reading this summary? Click here to contact a technical expert at Forrest Technical Coatings or visit our ESD products page.
ESD COATINGS MAKE WORKING SURFACES LESS PRONE TO SHORTS AND SPARKS
Build up of static electricity on surfaces create dangerous or difficult working environments. This is e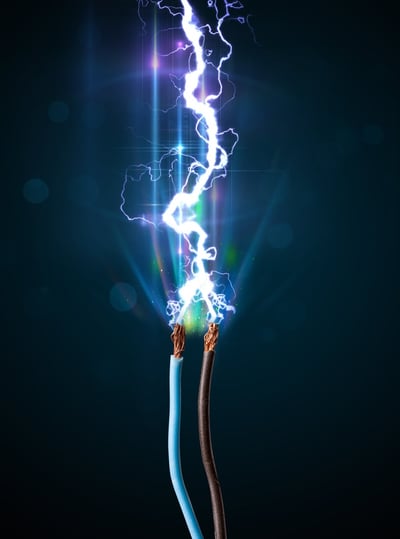 specially true when dealing with highly sensitive materials. ESD-coated surfaces prevent sparks, shorts, and sudden discharges that damage electronics or lead to explosions.
specially true when dealing with highly sensitive materials. ESD-coated surfaces prevent sparks, shorts, and sudden discharges that damage electronics or lead to explosions.
"ESD coatings are partially conductive, which means also partially resistive to current·flow, and can safely usher static electricity to an attached ground and prevent sparking." Dr. Sasha Tavenner Kruger, Research Chemist at Forrest Technical Coatings, explains to Powder Coated Tough Magazine in the July-August 2019 Issue.
Below are highlights from the full article published on the Powder Coating Tough website.
"By being only partially conductive, built-up charges don't tend to jump to the coated surface all at once, as can happen with fully conductive materials like metals. In other words, the rate of charge transfer is modified (slowed) by the ESD coating. However, ESD coatings are conductive enough that static electricity can't build up on them - the charges are dissipated."
Dr. Tavenner Kruger suggests ElectroStatic Dissipative Coatings for use in situations that benefit from a dissipated charge including:
WHERE ARE ELECTROSTATIC DISSIPATIVE COATINGS COMMONLY USED?
Electronics Workbenches:
Integrated circuits are notoriously prone to shock damage. This is why they arrive packaged in antistatic bags. An ESD coated workbench can prevent a lot of unintended damage.
Equipment housings, particularly for electronics or high voltage parts:
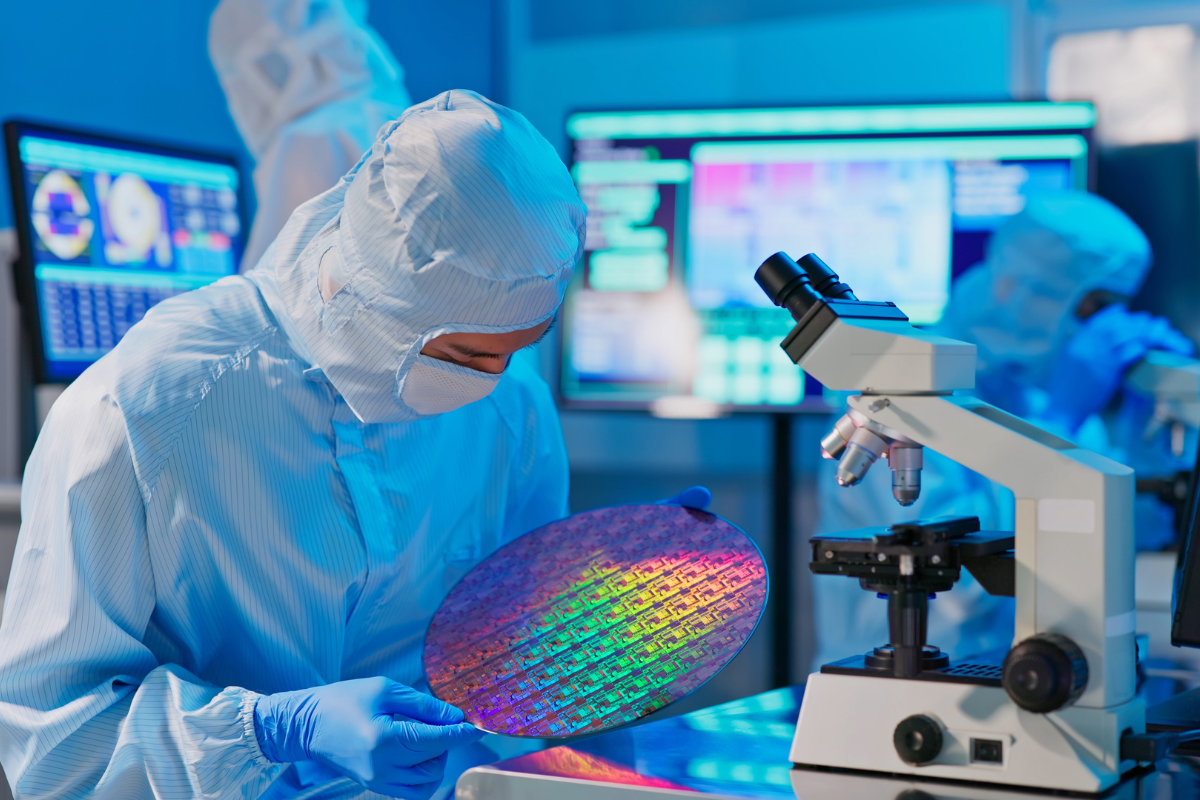
Semiconductor test equipment, for example, is housed in ESD-coated cabinets to prevent stray charges from damaging the delicate semiconductor parts being tested.
Garment or other factories that use racks of plastic bags:
In the absence of charge dissipation, the bags can become so charged that they cannot be separated from one another. ESD coatings on work surfaces (which are grounded so that chargecan flow away) can reduce the static cling of the plastic, leading to easier part separation and less of a shock hazard for the workers who must handle the parts.
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of circuits:
Some circuits produce signals in radio or shorter wavelengths which can interfere with other electronic circuits. Enclosing such circuits in a conductive or ESD (partially conductive) enclosure can, through the Faraday effect, reduce the signal leakage to the point of no longer interfering with other circuits in the area. Conversely, if a sensitive circuit is surrounded by noisy electromagnetic signal sources it can be protected from them by an ESD-coated enclosure. Device manufacturers
design and coat such enclosures and can use ESD coatings to accomplish EMI shielding.
Anywhere with dry winter weather:
Due to reduced carrying capacity for water in cold winter air, static shocks can increase, even in processes that don't show this behavior during other parts of the year. ESD-coated furniture, equipment cases, handles, and other parts can make the seasonal change less painful.
ESD coatings can be found in many forms. These include powder coatings, waterborne, solvent-borne, and UV-cure. Ranges of resistance typically fall within 106 to 1011 ohms, and an individual coating will usually have a slightly tighter specification than the whole range. The components which make the coating appropriate for ESD use are conductive and are loaded only to the degree needed to make the overall coating “conductive enough” for the specified range.
Visit FORREST's ESD Coatings product page to learn more about our powder coatings with electrostatic properties.
If you enjoyed this summary, read the original publication on the Powder Coated Tough website.






 specially true when dealing with highly sensitive materials.
specially true when dealing with highly sensitive materials.